Fabric I/O Naming (.xml)
The XML-based description language is used to describe
I/O names for an FPGA fabric when creating a top-level wrapper
I/O connections between the fabric and top-level wrappers
Using the description language, users can customize the I/O names for each pin/port of an FPGA fabric, including dummy pins (not from an FPGA fabric but required for system integration).
Under the root node <ports>, naming rules can be defined line-by-line through syntax <port>.
<ports>
<port top_name="<string>" core_name="<string>" is_dummy="<bool>" direction="<string>"/>
</ports>
Note
If you do not need to rename a port of an FPGA fabric, there is no need to define it explicitly in the naming rules. OpenFPGA can infer it.
Please be aware of the following restrictions:
Note
Please note that when naming rules should be applied to a port at its full size. For example, given a port of in[0:31], naming rules should cover all the 32 bits.
Note
Please note that we currently only supports port splitting at the top-level wrapper. For example, there is a port a[0:9] from the FPGA fabric, it can be split to a0[0:4] and a1[0:4] at the top-level wrapper.
Warning
Port grouping is NOT supported yet. For example, there are ports b[0:7] and c[0:7] from the FPGA fabric, it can NOT be grouped to a port bnc[0:15] at the top-level wrapper.
Syntax
Detailed syntax are presented as follows.
- top_name="<string>"
Define the port name and width which will appear in the top-level wrapper. For example,
top_name="a[0:2]"
- core_name="<string>"
Define the port name and width which exists in the current FPGA fabric. For example,
Note
You can find the available ports in the current top-level module of FPGA netlists. See details in Fabric Netlists.
core_name="gfpga_pad_GPIO_PAD[0:2]"
- is_dummy="<bool>"
Define if the port is a dummy one in the top-level wrapper, which does not connect to any pin/port of the current FPGA fabric. For example,
Note
When a dummy port is defined.
core_nameis not required.is_dummy="true"
- direction="<string>"
Direction can be
input|output|inout. Only applicable to dummy ports. For example,direction="input"
Example
Fig. 76 shows an example of a top-level wrapper with naming rules, which is built on top of an existing FPGA core fabric. There is a dummy input port at the top-level wrapper.
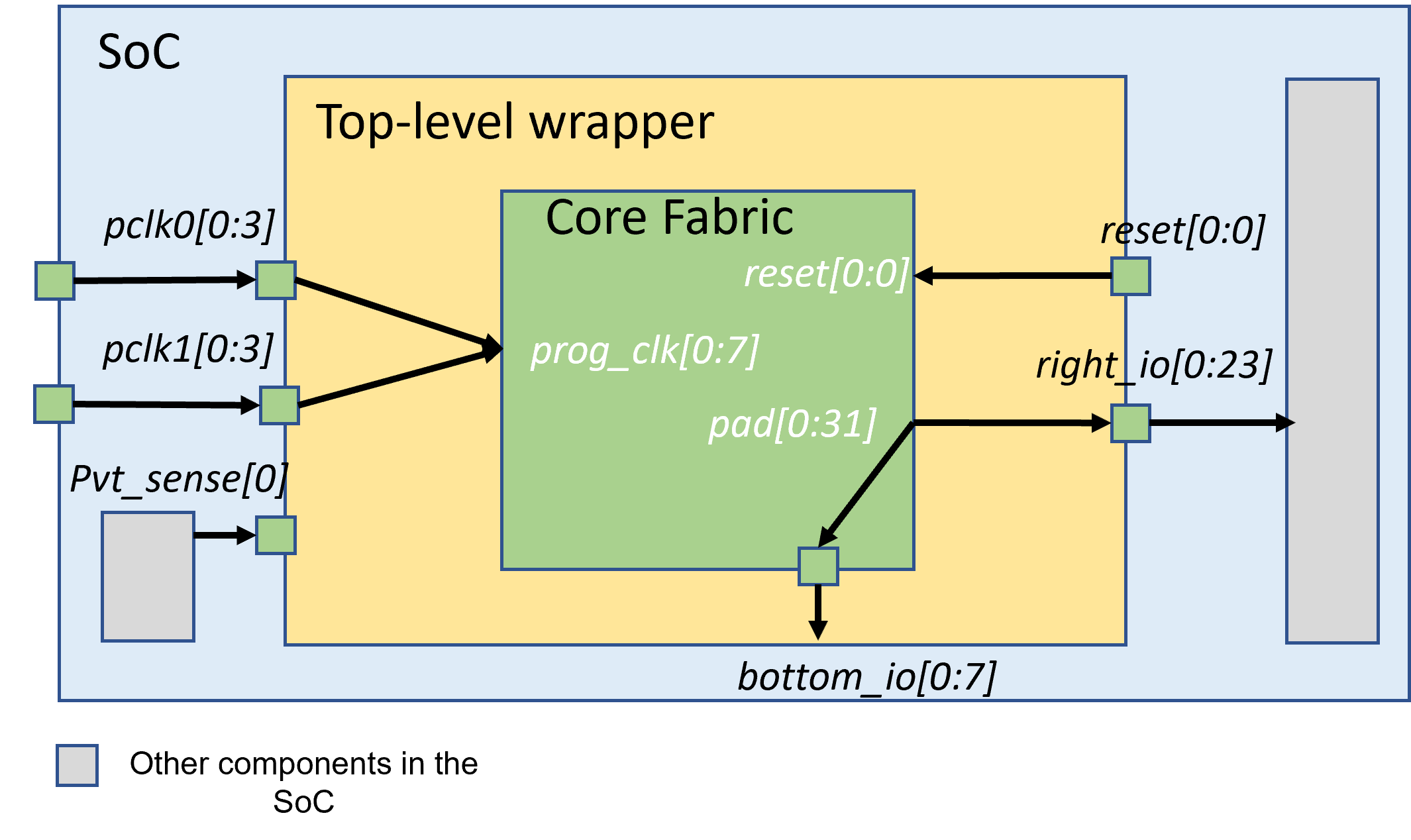
Fig. 76 Example of a top-level wrapper: how it interfaces between SoC and an existing FPGA core fabric
The I/O naming in the Fig. 76 can be described in the following XML:
<ports>
<port top_name="pclk0[0:3]" core_name="prog_clk[0:3]"/>
<port top_name="pclk1[0:3]" core_name="prog_clk[4:7]"/>
<port top_name="right_io[0:23]" core_name="pad[0:23]"/>
<port top_name="bottom_io[0:7]" core_name="pad[24:31]"/>
<port top_name="pvt_sense[0:0]" is_dummy="true" direction="input"/>
</ports>
Note that since port reset[0:0] require no name changes, it is not required to be defined in the XML.